CSW63 | Justice for Women
SIDE EVENT Justice for Women: Launch of the High-level Group Report
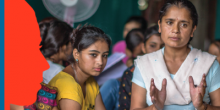
Gender inequality is an affront to human dignity, a challenge to the rule of law and an obstacle to development. Denying women of their rightful place in society – by depriving them of equal access to education, justice or livelihood – means robbing societies of the talent and potential of half of their members. In securing every social need from peace to food, the role of women has been shown to be paramount.
Although gender equality is increasingly a feature of national Constitutions, the law often continues to restrict women's rights and freedoms, dictates their submission to male relatives, or limits what they may own or inherit.
SIDE EVENT Justice for Women: Launch of the High-level Group Report
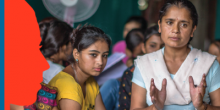
SIDE EVENT Women Delivering Justice: Investing in Women Justice Professionals for the Achievement of the 2030 Agenda

Over 50 women judges, representing chapters of the International Association of Women Judges across the African continent, convened to discuss the critical role and contribution women justice professionals play in adjudicating cases of gender-based violence at a regional conference in Nairobi from November 29 to December 1, 2018.

ROME, November 20, 2018 – “The quality of justice for women improves when women are not only consumers of justice, but also providers of justice,” remarked IDLO’s Director-General Irene Khan, launching a new report during IDLO’s annual Partnership Forum.
After breakfast every day Shabnum* sews chappan, a traditional coat worn by men and women in Afghanistan. In the afternoon, she embellishes the chappans with intricate needlework patterns to sell to interested buyers in Kabul.

On November 25, 2018, community-based organizations, non-governmental actors and representatives from the legal community convened in Mandalay, Myanmar for a special community theater performance raising awareness about violence against women.

“There are silver threads which the international community has woven into a tapestry known as the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development,” remarked IDLO’s Director-General Irene Khan at the opening of IDLO’s 2018 Partnership Forum. “At the heart of this tapestry is access to justice and the rule of law.”






|
Policy Statements
|
|
Policy Statements
|