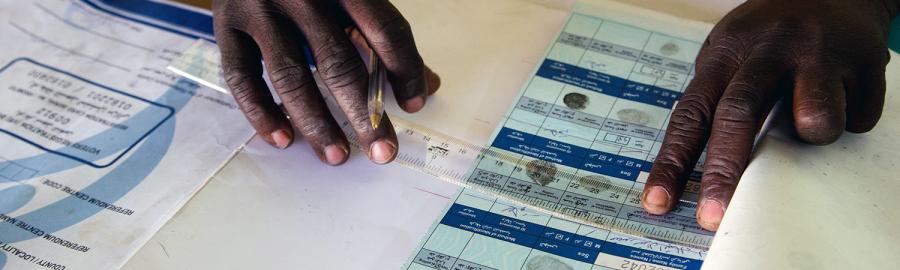
Youth Day: No Development Without Youth Development
The United Nations marks International Youth Day today (August 12) – an opportunity to recognize youths’ contribution to enhancing their communities and global society. Half of the world population is under 25. Almost two-billion people are under 14, the overwhelming majority of whom live in the developing world.